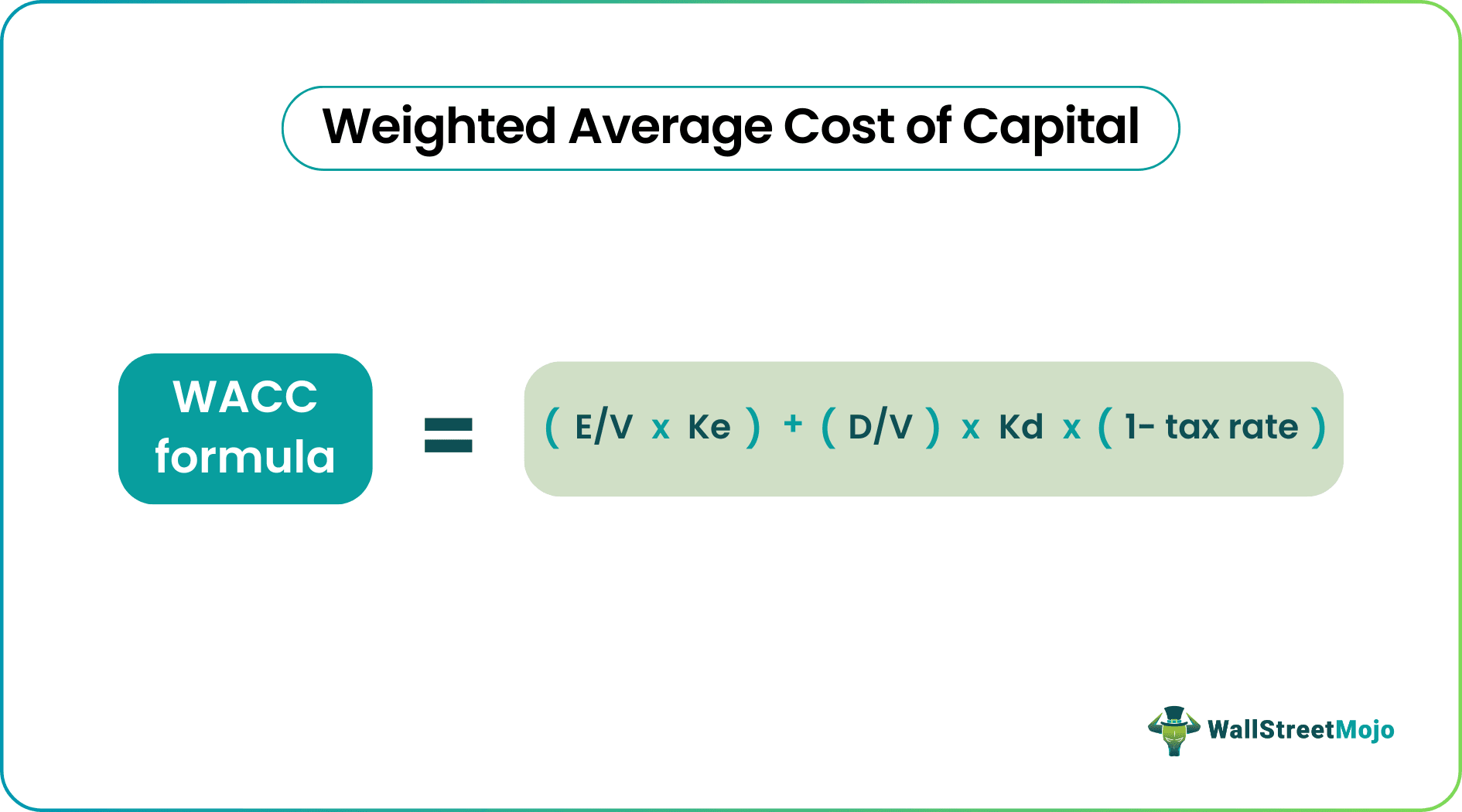
The weighted average cost of capital (WACC) is the average rate of return a company is expected to pay to all its shareholders, including debt holders, equity shareholders, and preferred equity shareholders. WACC Formula = [Cost of Equity * % of Equity] + [Cost of Debt * % of Debt * (1-Tax Rate)].

WACC is very useful if we can deal with the above limitations. It is exhaustively used to find the DCF valuation of the company. However, WACC is a bit complex and needs a financial understanding to calculate the Weighted Average Cost of capital accurately. Only depending on WACC to decide whether to invest in a company or not is a wrong idea.
Table of Contents
Weighted Average Cost of Capital Explained
WACC is the weighted average of a company’s debt and its equity cost. Weighted Average Cost of Capital equation assumes that capital markets (both debt and equity) in any given industry require returns commensurate with the perceived riskiness of their investments. But does WACC help the investors decide whether to invest in a company or not?
To understand the Weighted Average Cost of Capital, let’s take a simple example.
Suppose you want to start a small business! You go to the bank and ask if you need a loan to start. A bank looks at your business plan and tells you that it will lend you the loan, but there is one thing that you need to do. Bank says that you need to pay 10% interest over and above the principal amount you borrow. You agree, and the bank lends you the loan.
You agreed to pay a fee (interest expense) to avail the loan. This “fee” is the “cost of capital” in simple terms.
As businesses need a lot of money to invest in expanding their products and processes, they need to source money. They source money from their shareholders in the form of Initial Public Offerings (IPO), and they also take a loan from banks or institutions. Companies need to pay the cost to have this large sum of money. We call this the cost of capital. If a firm has more than one source which they take funds from, we need to take a weighted average of the cost of capital.

Many investors don’t calculate WACC because it’s a little more complex than the other financial ratios. But if you are one of those who would like to know how weighted average cost of capital (WACC) works, here’s the formula for you.
WACC Formula = (E/V * Ke) + (D/V) * Kd * (1 – Tax rate)
The equation may look complex, but it will begin to make sense as we learn each term. Let’s begin.
Let’s start with the E, the market value of equity. How should we calculate it? Here’s how –
Now, let’s understand the meaning of the market value of debt, D. How to calculate it?
As there are so many complexities in WACC calculation, we will take one example each for calculating all the portions of the weighted average cost of capital. Then we will take one final example to ascertain the WACC.
You can download this WACC Calculation - Excel Template here –
WACC Calculation - Excel Template Download TemplateStep # 1 – Calculating Market Value of Equity / Market Capitalization
Here are the details of Company A and Company B –
| In US $ | Company A | Company B |
| Outstanding Shares | 30000 | 50000 |
| Market Price of Shares | 100 | 50 |
In this case, we have been given both the numbers of outstanding shares and the market price of shares. So let’s calculate the market capitalization of Company A and Company B.
| In US $ | Company A | Company B |
| Outstanding Shares (A) | 30000 | 50000 |
| Market Price of Shares (B) | 100 | 90 |
| Market Capitalization (A*B) | 3,000,000 | 4,500,000 |
Now we have the market value of equity or market capitalization of Company A and Company B.
Step # 2 – Finding Market Value of Debt
Let’s say we have a company for which we know the total debt. Total Debt (T) = US $100 million. To find the market value of debt, we need to check if this debt is listed.
If yes, then we can directly pick the latest traded price. So, for example, if the trading value was $84.83 for a face value of $100, then the market value of debt will be $84.83 million.
Step # 3 Calculate Cost of Equity
Cost of Equity = Rf + (Rm-Rf) x Beta
Cost of Equity = 4% + 6% x 1.5 = 13%
Step # 4 – Calculate the Cost of Debt
Let’s say we have been given the following information –
Let’s calculate the cost of debt.
Cost of Debt = (Risk Free Rate + Credit Spread) * (1 – Tax Rate)
Or, Kd = (0.04 + 0.02) * (1 – 0.35) = 0.039 = 3.9%.
Step # 5 – WACC Calculation
So after calculating everything, let’s take another example of WACC calculation (weighted average cost of capital).
| In US $ | Company A | Company B |
| Market Value of Equity (E) | 300000 | 500000 |
| Market Value of Debt (D) | 200000 | 100000 |
| Cost of Equity (Re) | 4% | 5% |
| Cost of Debt (Rd) | 6% | 7% |
| Tax Rate (Tax) | 35% | 35% |
We need to calculate WACC for both of these companies.
Let’s look at the WACC formula first –
WACC Formula = E/V * Ke + D/V * Kd * (1 – Tax)
Now, we will put the information for Company A,
weighted average cost of capital formula of Company A = 3/5 * 0.04 + 2/5 * 0.06 * 0.65 = 0.0396 = 3.96%.
WACC formula of Company B = 5/6 * 0.05 + 1/6 * 0.07 * 0.65 = 0.049 = 4.9%.
Now we can say that Company A has a lesser cost of capital (WACC) than Company B. Depending on the return both of these companies make at the end of the period, we would be able to understand whether, as investors, we should invest into these companies or not.
Assuming that you are comfortable with the basic WACC examples, let us take a practical example to calculate the WACC of Starbucks. Please note that Starbucks has no preferred shares and hence, the WACC formula to be used is as follows –
WACC Formula = E/V * Ke + D/V * Kd * (1 – Tax Rate)
Step 1 – Find the Market Value of Equity
Market Value of Equity = Number of shares outstanding x current price.
The market value of equity is also market capitalization. Let us look at the total number of shares of Starbucks –

Step 2 – Find the Market Value of Debt
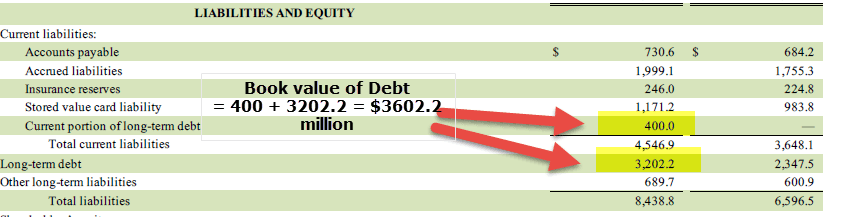
Let us look at the balance sheet of Starbucks below. As of FY2016, the book value of debt is current.
As of FY2016, book value of Debt is the current portion of long-term debt ($400) + Long Term Debt ($3202.2) = $3602.2 million.
However, when we further read about Starbucks debt, we are additionally provided with the following information –
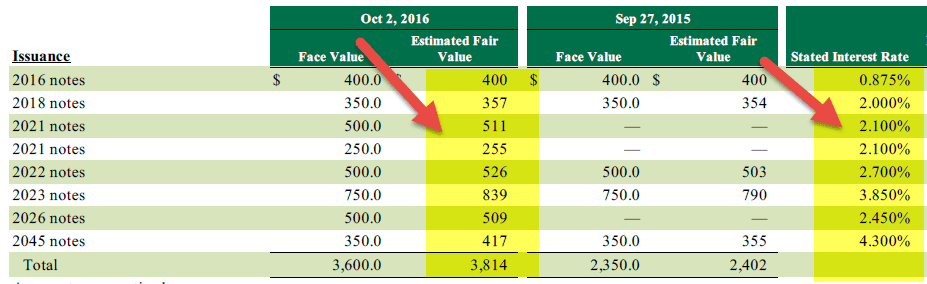
As we note above, Starbucks provides the fair value of the Debt ($3814 million) as well as the book value of debt. Therefore, in this case, it is prudent to take the fair value of debt as a proxy for the market value of debt.
Step 3 – Find the Cost of Equity
As we saw earlier, we use the CAPM model to find the cost of equity.
Ke = Rf + (Rm – Rf) x Beta
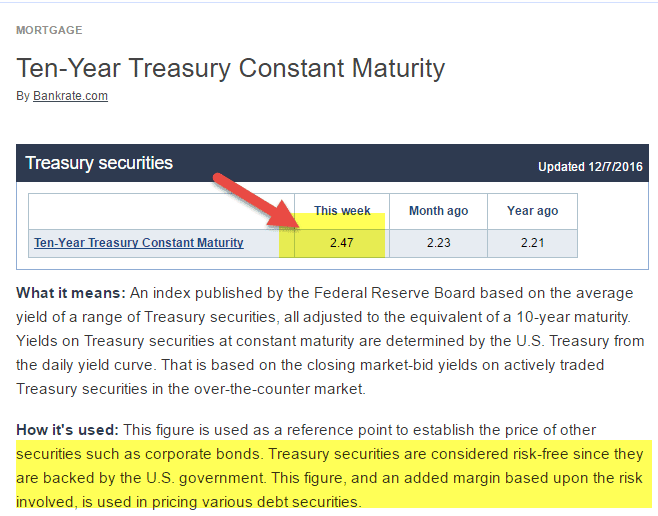
Risk-Free Rate
Here, I have considered a 10-year Treasury Rate as the Risk-free rate. However, some analysts also take a 5-year treasury rate as the risk-free rate. Please check with your research analyst before taking a call on this.
 Risk Free Rate Startbucks WACC" />
Risk Free Rate Startbucks WACC" />
Equity Risk Premium (Rm – Rf)
Each country has a different Equity Risk Premium. Equity Risk Premium primarily denotes the premium expected by the Equity Investor.
For the United States, Equity Risk Premium is 6.25%.
Beta
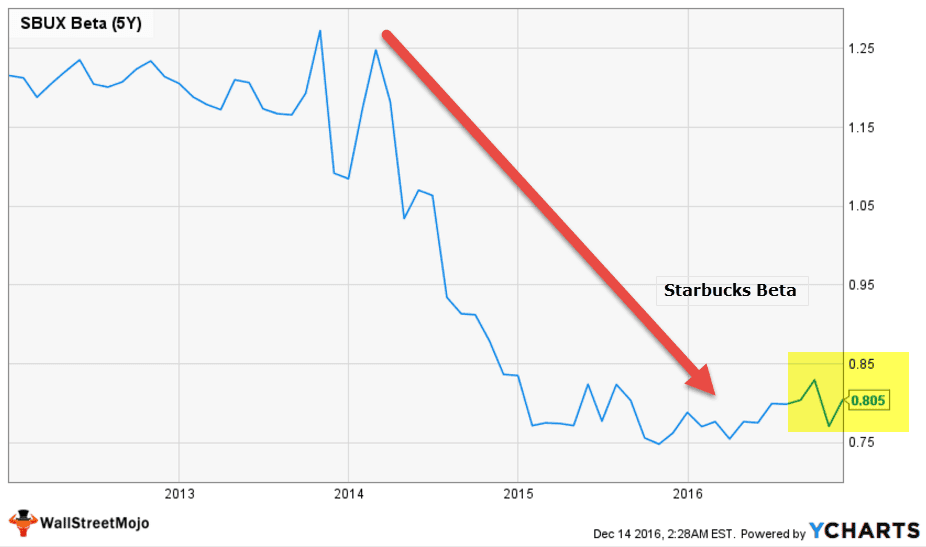
Let us now look at Starbucks Beta Trends over the past few years. The beta of Starbucks has decreased over the past five years. This means that Starbucks stocks are less volatile as compared to the stock market.
We note that the Beta of Starbucks is at 0.805x
With this, we have all the necessary information to calculate the cost of equity.
Cost of Equity = Ke = Rf + (Rm – Rf) x Beta
Ke = 2.47% + 6.25% x 0.805
Cost of Equity = 7.50%
Step 4 – Find the Cost of Debt
Let us revisit the table we used for the fair value of debt. We are additionally provided with its stated interest rate.
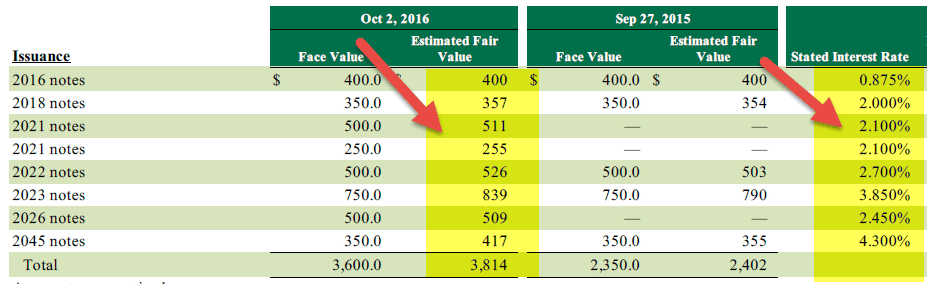
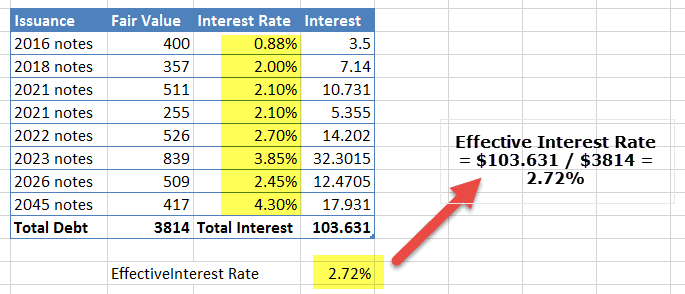
Using the interest rate and fair value, we can find the weighted average interest rate of the total fair value of Debt ($3,814 million)
Step 5 – Find the Tax Rate
We can easily find the effective tax rate from the Income Statement of Starbucks.
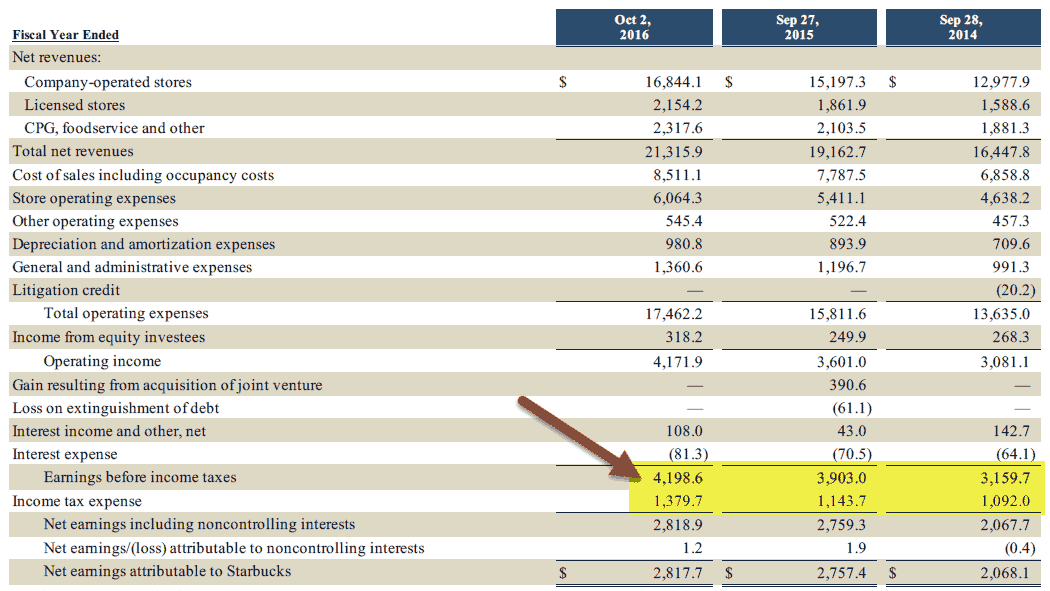
For FY2016, Effective tax rate = $1,379.7 / $4,198.6 = 32.9%
Step 6 – Calculate the weighted average cost of capital (WACC) of Starbucks
We have collected all the information that is needed to calculate WACC.
WACC Formula = E/V * Ke + D/V * Kd * (1 – Tax Rate)
= (86,319.8/90133.8) x 7.50% + (3814/90133.8) x 2.72% x (1-0.329)
= 7.26%
The interpretation depends on the company’s return at the end of the period. If the company’s return is far more than the Weighted Average Cost of Capital Equation, then the company is doing pretty well. But if there is a slight profit or no profit, the investors need to think twice before investing in the company.
Here is another thing you need to consider as an investor. If you want to calculate the Weighted Average Cost of Capital, there are two ways you can use. The first is the book value, and the second is the market value approach.
As you can see that if you consider the calculation using market value, it’s far more complex than any other ratio calculation; you can skip and decide to find the weighted average cost of capital (WACC) on the book value given by the company in their Income statement and in the Balance Sheet. However, book value calculation is not as accurate as the market value calculation. In most cases, market value is considered for the Weighted Average Cost of Capital (WACC) calculation for the company.
Sensitivity Analysis – WACC & Share Price
WACC is widely used in Discounted Cash Flow Valuation. As an analyst, we do try to perform sensitivity analysis in Excel to understand the fair value impact along with changes in WACC and growth rate.
Below is the Sensitivity Analysis of Alibaba IPO Valuation with two variables weighted average cost of capital (WACC) and growth rate.
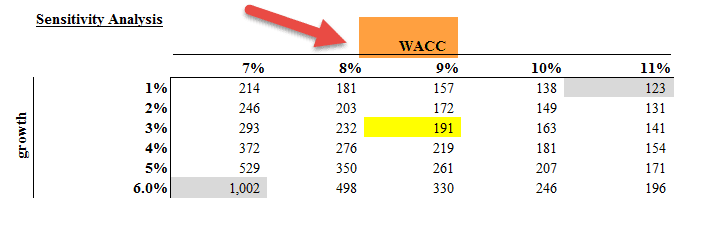
Some of the observations that can be made about WACC –
The Weighted Average Cost of Capital calculator holds immense significance in corporate finance and investment decision-making due to its multifaceted role in assessing cost-efficiency, guiding financing choices, and evaluating project feasibility. Let us understand its importance through the points below.
Despite the advantages and importance mentioned about the weighted average cost of capital calculator, there are a few limitations that are discussed through the points below.